
HOW TO USE TELNET TO TEST PORT 443 UPDATE
If custom ports are being used please update the commands accordingly. The instructions below use the default ports of 8014, 443, and 2967 for communication.
The File ContentInfo.txt exists on the SEPM and lists the content updates that the SEPM has. I’d be very interested in hearing about our readers’ other methods used to test network connections.Use a browser and the contentinfo.txt for troubleshooting the connection and the transfer of files between computers. I hope this article was beneficial in learning about testing TCP services with telnet. For this reason, it’s a good idea to configure internal firewalls with reject rules and external ones, while facing public networks with drop rules. As I described earlier, since this method is more difficult to troubleshoot, it’s more appropriate to slow down hostile users that are scanning a network in the hopes of finding vulnerabilities to exploit. The second method is to silently drop the packets, acting as if the host is unreachable. When a connection is rejected, the firewall tells the source that the destination host is not allowing incoming connections to specific port(s). Difference between reject and drop in firewall configurationsįirewalls can block connections via two methods: reject or drop. Network firewalls are sophisticated appliances that can inspect a large amount of throughput data adding little delay. Most modern operating systems, like Windows, Mac, or Linux, have available such a service.Ī network firewall is a dedicated device that is installed on a specific network segment to protect one or more private networks that reside behind it. The goal of such firewall is to protect the host itself where the firewall is running. In this case, further troubleshooting is required, such as verifying with a traceroute from the client side where the connection is interrupted or getting in touch with the administrator of the remote host to ask whether the remote service is running and allowed by any firewall in between.īefore concluding this post, I would like to explain two important concepts related to firewalls … Difference between host firewalls and network firewallsĪ host firewall runs on a computer, or server, to block or allow incoming connections to specific local services. This case is more difficult to troubleshoot because it could be either that:ġ) a network or host firewall is dropping incoming connections 2) the remote is down 3) network connectivity between the client and server is unavailable for some reason. In this other scenario, telnet is not returning any message. When troubleshooting client connectivity issues to a TCP service, another possible scenario is the following: In this case, telnet is returning the message “Connection refused” to communicate to the user that a firewall is blocking connections to the specified TCP port on the remote host.
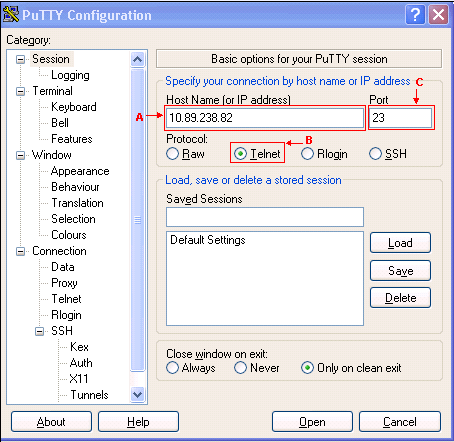
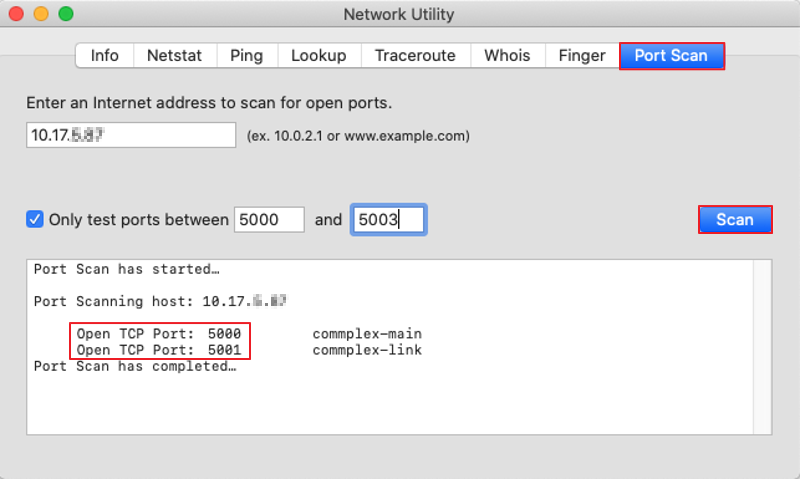
Let’s see what happens when a firewall in between is rejecting connections: If the service is running with no firewalls in-between blocking incoming connections, the telnet command will return the following prompt:Īs you can see, the telnet command returns the resolved IP address associated to the provided hostname, and give notice of the escape characters, ‘ SHIFT ]’, that can be used to terminate the connection. The telnet command syntax is the following: telnet ]įor example, if you want to test connectivity to a remote service using port 20011 on host, you’ll have to type: telnet 20011 In a client-server architecture, you can use telnet to make sure that no firewalls in between are blocking incoming connections to the server. All information exchanged in a telnet session between a client and server is unencrypted and, for this reason, in the last years this application has been replaced by SSH, which provides the same type of service, but encrypted, as it’s based on the Secure Socket Layer (SSL) protocol.Īlthough telnet has become obsolete for remote administration purposes this application is still widely used to verify connectivity to remote services that are based on TCP. By default, a telnet server listens on port 23 for incoming connections from clients. This application is based on the connection-oriented Transmission Control Protocol (TCP). Network and system administrators use this application to configure and administer network devices such as servers, routers, switches, etc. Telnet is an application that is used to connect to a remote host’s command line terminal interface.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
